1. What is LED Viewing Angle?
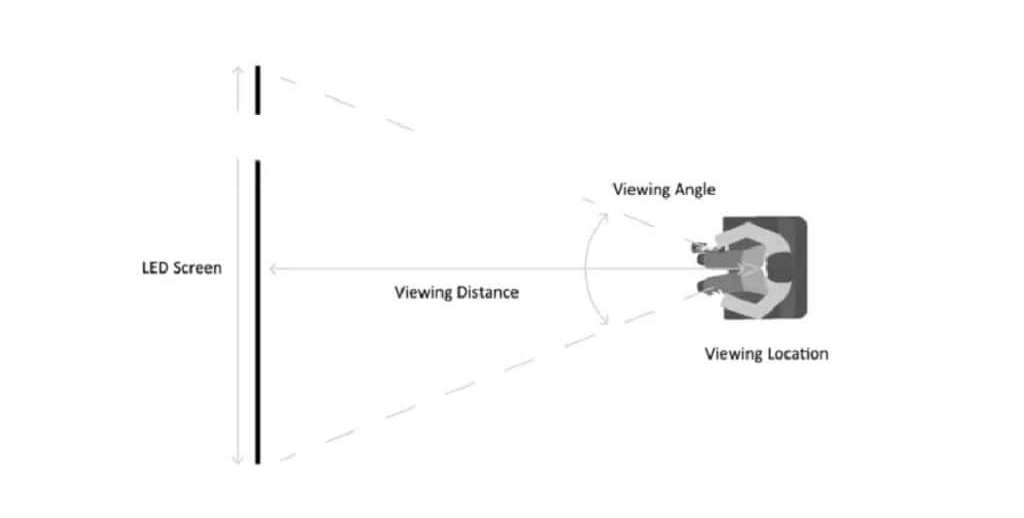
The LED viewing angle refers to the maximum angular range within which, under the premise of ensuring that the screen display content remains clear, the color is full, and key indicators such as brightness and contrast are stable, viewers can obtain a satisfactory visual experience whether they are viewing from the front or deviating to the left, right, up, or down. In other words, it directly determines the size of the area where the LED display can provide a high – quality display effect regardless of where the audience is located in practical applications.
The viewing angle not only affects the coverage in occasions such as advertising and public information display but also impacts the viewing experience of the audience. For example, on an advertising screen in a busy commercial area, a wide viewing angle can ensure that pedestrians from all directions can capture the advertising information, thus greatly enhancing the communication effect. In an immersive environment such as a stage performance or a cinema, it is even more crucial to ensure that all audience members can see an undistorted picture.
2. Composition of LED Viewing Angle
The LED viewing angle is mainly composed of two directions: horizontal and vertical.
Horizontal Viewing Angle
The horizontal viewing angle describes the range extended from the front of the screen to the left and right. Within this range, the screen display effect remains basically stable, for example, the brightness and color do not deviate significantly. If the horizontal viewing angle of an LED video wall is 140°, it means that within the area 70° to the left and right of the front, the audience can experience a relatively ideal display effect.
Vertical Viewing Angle
The vertical viewing angle is the angular range of deviation from the front of the screen upwards or downwards. When the viewer’s position gradually deviates from the front, as long as the screen display effect (such as image clarity and contrast) does not deteriorate significantly, the deviation angle is within the effective range. For example, if the vertical viewing angle is 120°, it means that the screen can maintain a good visual effect within 60° upwards or downwards from the front.
3. Classification of Viewing Angles of LED Display
According to different technical specifications and application scenarios, the viewing angles of LED displays are usually divided into the following categories:
Narrow Viewing Angle
The horizontal and vertical angles of this type of display are generally between 90° and 120°. Although it can present an excellent display effect within the specified angle, once outside this range, the display quality will decline rapidly. Therefore, LED displays with a narrow viewing angle are usually applied in occasions where the viewing direction is clearly defined, such as indoor monitoring display terminals, and only viewers in a specific direction can clearly see the screen content.
Medium Viewing Angle
For LED displays with a medium viewing angle, their horizontal and vertical angles are usually between 120° and 140°. This type of display can meet the viewing needs in most ordinary indoor environments, such as the screen in a conference room, where participants can obtain a good visual experience within a certain area.
Wide Viewing Angle
The horizontal and vertical angles of LED displays with a wide viewing angle are generally between 140° and 160°. They are suitable for occasions where multiple people need to view from different angles simultaneously, such as school multimedia classrooms. Even if the viewers are standing in a relatively off – center position, they can still enjoy a good display effect.
Ultra Wide Viewing Angle
The ultra – wide viewing angle usually refers to horizontal and vertical angles greater than 160°, and can even reach 178°, almost achieving a full – view angle. This type of display is commonly seen in large – scale occasions with extremely high requirements for the viewing experience, such as the central display screen in a large shopping mall or the background of an event stage. No matter from which angle it is viewed, it can present an excellent picture.
4. The Role of Viewing Angle in LED Screen
Display Effect
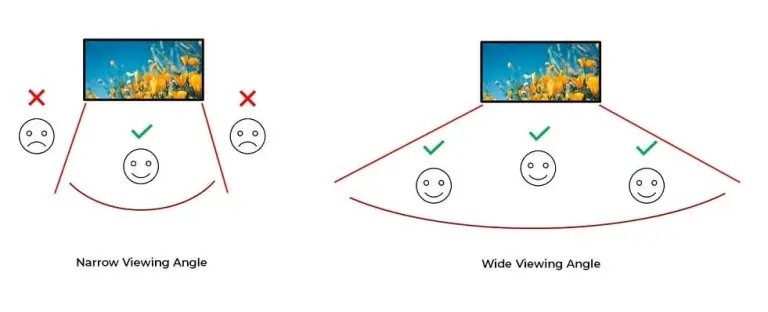
When the viewing angle deviates from the front of the screen, color deviation, image stretching, or distortion may occur. Displays with a narrow viewing angle tend to have these problems at a relatively small deviation angle, while displays with a wide viewing angle can maintain a stable display effect within a larger angle range, thus improving the overall viewing experience.
Screen Brightness
The brightness of the LED display also gradually decreases as the viewing angle increases. This is mainly because the light – emitting characteristics of the LED determine the uneven distribution of light intensity in different directions. Comparatively, the brightness of narrow – angle LEDs decays faster, while wide – angle LEDs can maintain a relatively balanced brightness performance within a larger range.
Trade off between Angle and Cost
Generally speaking, wide angle LEDs have a relatively high cost due to their higher technical difficulty and strict production process requirements. Narrow angle LEDs, on the other hand, have a lower cost and are suitable for occasions where only fixed direction viewing is required.
5. Factors Affecting the Viewing Angle of LED Display
LED Packaging TechnologyOptimization of LED Chips and Packaging
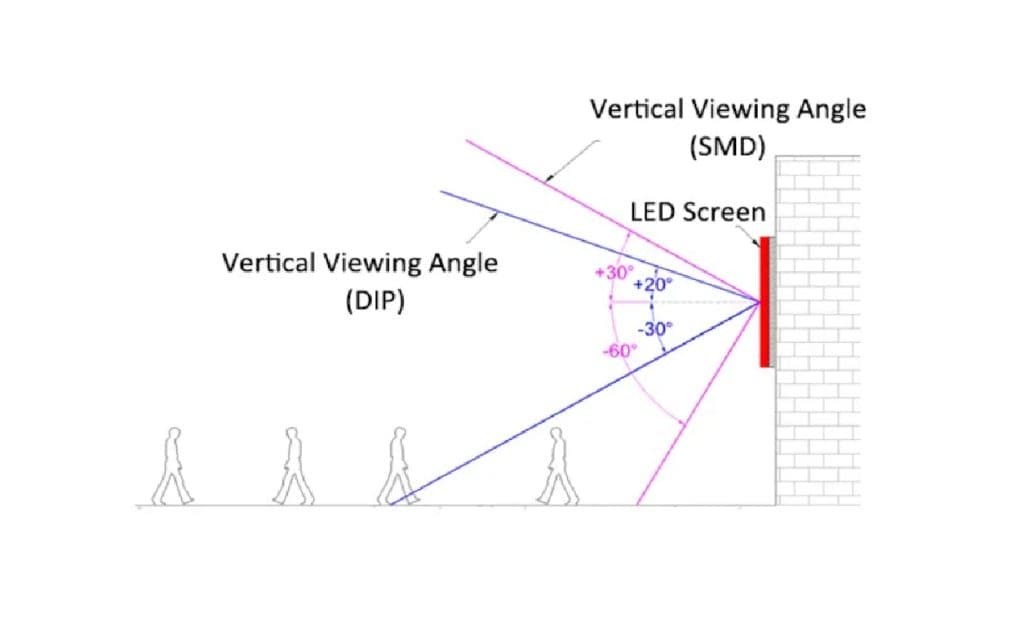
DIP (Dual – In – line Package): It has a relatively large volume, a luminous angle of usually around 120°, and good heat dissipation performance. However, it has limitations in large – size and high resolution applications.
SMD (Surface-Mounted Device): The lamp beads are small in size, enabling a higher pixel density. The luminous angle is generally between 140° and 160°, and it is widely used.
COB (Chip-on-Board): The LED chips are directly packaged on the circuit board, reducing the blockage of light by packaging materials. It can usually achieve a viewing angle of more than 160°, and at the same time, it has better protection and stability, but the cost is high.
By improving the internal structure of the chip (such as adopting a new quantum well structure or optimizing the electrode design) and selecting packaging materials with high light transmittance and low refractive index, the efficiency and uniformity of the emitted light can be improved, thereby expanding the viewing angle.
Adjustment of Display Module Design
Reasonably planning the arrangement of lamp beads, such as staggered or circular layouts, can improve the light distribution. At the same time, using a well – designed mask (with special textures or curvatures) can also effectively guide and diffuse the light, enhancing the overall viewing angle.
Optimization of Control System and Driver
Through advanced grayscale control algorithms and high – performance driver chips, the screen brightness and color can be adjusted in real – time according to the viewing angle to compensate for the brightness decay and color deviation caused by the angle change, thus improving the display consistency at different angles.
Viewing Angle Optimization Technology
For example, a viewing – angle optimization film can refract and scatter light through a special optical design, making more light evenly distributed over a wider range. In addition, optimizing and adjusting the display content according to different installation positions and viewing angles can also make up for the information loss caused by insufficient viewing angles to a certain extent.
6. How to Measure the Viewing Angle of an LED Display?
When measuring the viewing angle of an LED display, the commonly used methods mainly include the brightness measurement method and the contrast measurement method.
Brightness Measurement Method
Use a professional luminance meter to gradually deviate from the front to the left, right, up, and down at a certain distance (such as 3 meters), and record the screen brightness every certain angle (for example, 5°). When the brightness drops to 50% of the brightness from the front, the angle is considered the viewing angle.
Contrast Measurement Method
By measuring the contrast of the screen image at different angles, when the contrast drops to a certain standard value (for example, 10:1), record this angle as the viewing angle. This method can more comprehensively reflect the comprehensive performance of the screen at different viewing angles.
The basic steps usually include: installing the display in a standard test environment and adjusting it to the standard brightness and contrast; calibrating and using professional instruments to measure the brightness or contrast in the horizontal and vertical directions in turn; recording data until the set critical value is reached, so as to determine the viewing – angle range.
7. How to Optimize the Viewing Angle of an LED Display?
To improve the viewing angle of an LED display, the following aspects can be optimized
Select the Appropriate LED Chip and Packaging Method
According to the requirements of different application scenarios, select LED chips with a wide viewing – angle characteristic. For applications with high requirements, preferentially adopt chips with a new structure, high luminous efficiency, and good uniformity. At the same time, choosing a display with COB packaging can better achieve wide – angle display.
Adjust the Display Module Design
Optimize the layout of lamp beads. Especially for large – size displays, using a staggered arrangement or a special geometric arrangement can improve the light distribution. In addition, improving the mask design (selecting materials with high light transmittance and special optical effects) can also effectively expand the viewing angle.
Adjust the Display Content and Control System
Optimize the display content according to the installation position and viewing angle. For example, place important information in the center of the screen to avoid missing key information in the edge part. At the same time, upgrade the control system. Through advanced grayscale control algorithms and adaptive adjustment technologies, compensate for display deviations at different angles in real – time, thereby enhancing the overall visual effect.
8. How to Select the Appropriate Viewing Angle According to Your Application?
Different scenarios have different requirements for the viewing angle:
Stage Performances and Event Displays: Usually, an ultra – wide viewing angle (more than 160°) is required to ensure that the audience in every corner can clearly see the performance content and maintain high brightness and high contrast at large angles.
Outdoor Advertising Screens: Generally, a wide viewing angle (140° – 160°) is needed to adapt to the viewing crowd from different directions and improve the coverage of advertising information.
Traffic and Highway Displays: To ensure that drivers can see key information at different angles, these displays generally need to reach a viewing angle of about 140°, and at the same time, they should have high brightness and fast response characteristics.
Conference Room and Classroom Displays: A medium viewing angle (120° – 140°) is usually sufficient because the audience is mainly concentrated within a specific range in front of the screen.
9. FAQs
a. What viewing angle should I choose?
This depends on the specific application scenario. For occasions where the viewing direction is relatively fixed, such as indoor monitoring, a narrow viewing angle (90° – 120°) may be sufficient. For medium – sized viewing occasions such as conference rooms and classrooms, a medium viewing angle (120° – 140°) is suitable. For large – scale events and outdoor advertising, a wide or ultra – wide viewing angle (more than 140°) is recommended.
b. Can the viewing angle of an LED display be optimized?
Certainly. By choosing the appropriate LED chip and packaging method, adjusting the design of the display module, optimizing the control system, and using technologies such as viewing – angle optimization films, the viewing angle of the LED display can be improved to a certain extent.
c. Does the viewing angle affect the brightness of the LED screen?
Yes. As the viewing angle gradually deviates from the front, the screen brightness will gradually decay. This decay rate is faster in narrow – angle displays, while wide – angle displays can maintain a relatively stable brightness within a large range.
d. When is it suitable to use narrow – angle LEDs?
When the application scenario has strict restrictions on the display direction, such as indoor monitoring terminals or specific industrial displays, where only specific – direction viewing is required, using narrow – angle LEDs can not only meet the requirements but also reduce costs.
10. Conclusion
In general, the viewing angle of an LED display is not only a key technical indicator but also directly affects the user’s viewing experience. Whether it is through hardware packaging, chip design, display module layout, or the application of intelligent control systems and viewing angle optimization technologies, improvements in each link can bring a wider viewing angle to meet the diverse requirements for display effects in different occasions. Selecting the appropriate viewing angle according to the actual use scenario and combining it with corresponding optimization measures can effectively improve the performance of the LED display in various complex environments and provide the audience with the best visual enjoyment.
Post time: Feb-06-2025





