LED displays are integrating into our daily lives at an unprecedented pace, with SMD (Surface Mounted Device) technology standing out as one of its key components. Known for its unique advantages, SMD LED display have gained widespread attention. In this article, RTLED will explore the types, applications, benefits, and future of SMD LED display.
1. What is SMD LED Display?
SMD, short for Surface Mounted Device, refers to a surface-mounted device. In the SMD LED display industry, SMD encapsulation technology involves packaging LED chips, brackets, leads, and other components into miniaturized, lead-free LED beads, which are directly mounted onto printed circuit boards (PCBs) using an automated placement machine. Compared to traditional DIP (Dual In-line Package) technology, SMD encapsulation has higher integration, smaller size, and lighter weight.
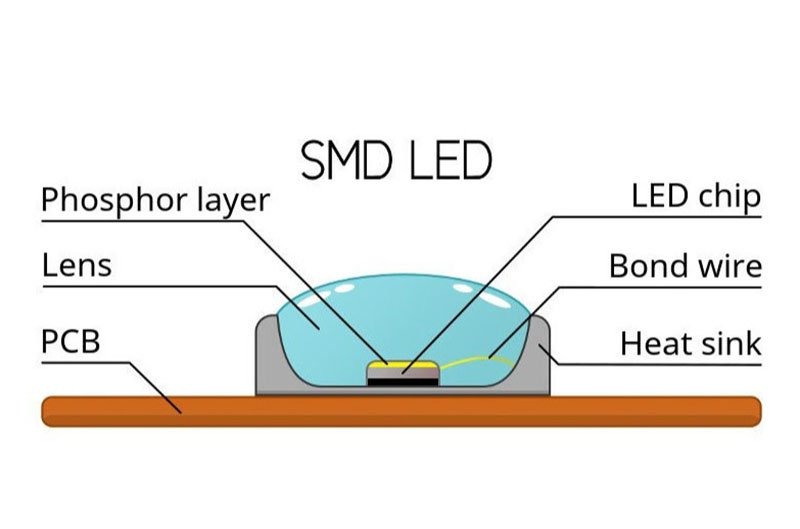
2. SMD LED Display Working Principles
2.1 Luminescence Principle
The luminescence principle of SMD LEDs is based on the electroluminescence effect of semiconductor materials. When current passes through a compound semiconductor, electrons and holes combine, releasing excess energy in the form of light, thus achieving illumination. SMD LEDs use cold light emission, rather than heat or discharge-based emission, which contributes to their long lifespan, typically over 100,000 hours.
2.2 Encapsulation Technology
The core of SMD encapsulation lies in “mounting” and “soldering.” LED chips and other components are encapsulated into SMD LED beads through precision processes. These beads are then mounted and soldered onto PCBs using automated placement machines and high-temperature reflow soldering technology.
2.3 Pixel Modules and Driving Mechanism
In an SMD LED display, each pixel is composed of one or more SMD LED beads. These beads can be monochrome (such as red, green, or blue) or bi-color, or full-color. For full-color displays, red, green, and blue LED beads are commonly used as the basic unit. By adjusting the brightness of each color through a control system, full-color displays are achieved. Each pixel module contains multiple LED beads, which are soldered onto PCBs, forming the basic unit of the display screen.
2.4 Control System
The control system of an SMD LED display is responsible for receiving and processing input signals, then sending the processed signals to each pixel to control its brightness and color. The control system typically includes signal reception, data processing, signal transmission, and power management. Through complex control circuits and algorithms, the system can precisely control each pixel, presenting vibrant images and video content.
3. Advantages of SMD LED Display Screen
High Definition: Due to the small size of the components, smaller pixel pitches can be achieved, improving image delicacy.
High Integration and Miniaturization: SMD encapsulation results in compact, lightweight LED components, ideal for high-density integration. This enables smaller pixel pitches and higher resolutions, enhancing image clarity and sharpness.
Low Cost: Automation in production reduces manufacturing costs, making the product more affordable.
Efficient Production: The use of automated placement machines greatly improves production efficiency. Compared to traditional manual soldering methods, SMD encapsulation allows faster mounting of large numbers of LED components, reducing labor costs and production cycles.
Good Heat Dissipation: SMD encapsulated LED components are directly in contact with the PCB board, which facilitates heat dissipation. Effective heat management extends the lifespan of LED components and improves display stability and reliability.
Long Lifespan: Good heat dissipation and stable electrical connections extend the lifespan of the display.
Easy Maintenance and Replacement: As SMD components are mounted on PCBs, maintenance and replacement are more convenient. This reduces the cost and time of display maintenance.
4. Applications of SMD LED Displays
Advertising: SMD LED displays are frequently used in outdoor advertisements, signage, and promotional activities, broadcasting ads, news, weather forecasts, etc.
Sports Venues and Events: SMD LED displays are used in stadiums, concerts, theaters, and other large events for live broadcasting, score updates, and video playback.
Navigation and Traffic Information: LED screen walls provide navigation and information in public transportation, traffic signals, and parking facilities.
Banking and Finance: LED screens are used in banks, stock exchanges, and financial institutions to display stock market data, exchange rates, and other financial information.
Government and Public Services: SMD LED displays provide real-time information, notifications, and announcements in government agencies, police stations, and other public service facilities.
Entertainment Media: SMD LED screens in cinemas, theaters, and concerts are used for playing movie trailers, advertisements, and other media content.
Airports and Train Stations: LED displays in transportation hubs like airports and train stations show real-time flight information, train schedules, and other updates.
Retail Displays: SMD LED displays in stores and malls broadcast product advertisements, promotions, and other relevant information.
Education and Training: SMD LED screens are used in schools and training centers for teaching, displaying course information, etc.
Healthcare: SMD LED video walls in hospitals and clinics provide medical information and health tips.
5. Differences between SMD LED Display and COB LED Display
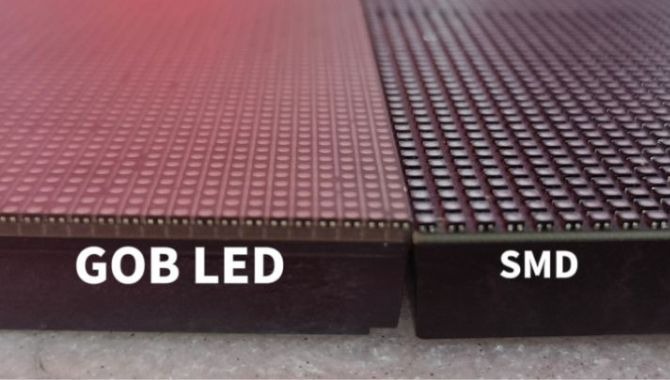
5.1 Encapsulation Size and Density
SMD encapsulation has relatively larger physical dimensions and pixel pitch, suitable for indoor models with pixel pitch above 1mm and outdoor models above 2mm. COB encapsulation eliminates the LED bead casing, allowing for smaller encapsulation sizes and higher pixel density, ideal for smaller pixel pitch applications, such as P0.625 and P0.78 models.
5.2 Display Performance
SMD encapsulation uses point light sources, where pixel structures may be visible up close, but color uniformity is good. COB encapsulation uses surface light sources, offering more uniform brightness, a wider viewing angle, and reduced granularity, making it suitable for close-range viewing in settings such as command centers and studios.
5.3 Protection and Durability
SMD encapsulation has slightly lower protection compared to COB but is easier to maintain, as individual LED beads can be replaced easily. COB encapsulation offers better dust, moisture, and shock resistance, and upgraded COB screens can achieve a 4H surface hardness, protecting against impact damage.
5.4 Cost and Production Complexity
SMD technology is mature but involves a complex production process and higher costs. COB simplifies the production process and theoretically reduces costs, but it requires significant initial equipment investment.
6. The Future of SMD LED Display Screens
The future of SMD LED displays will focus on continuous technological innovation to improve display performance, including smaller encapsulation sizes, higher brightness, richer color reproduction, and wider viewing angles. As market demand expands, SMD LED display screens will not only maintain a strong presence in traditional sectors like commercial advertising and stadiums but will also explore emerging applications such as virtual filming and xR virtual production. Collaboration across the industry chain will drive overall prosperity, benefiting both upstream and downstream businesses. Furthermore, environmental protection and intelligent trends will shape future development, pushing SMD LED displays towards greener, more energy-efficient, and smarter solutions.
7. Conclusion
In summary, SMD LED screens are the preferred choice for any type of product or application. They are easy to set up, maintain, and operate, and are considered more convenient than traditional options. If you have further questions, feel free to contact us now for assistance.
Post time: Sep-23-2024




